Biological Clocks in Mosquitoes
|
Experimental regimes
LD 4:20, five females, studied from 5-6 days post-emergence (5-6
December 1968) and recorded for days eight to ten.
LD 8:16, nine females, studied from 3-4 days post-emergence (31
October 1968) and recorded for days seven and eight.
LD 12:12 to LD 16:8, nine females, studied from 3-4 days
post-emergence (31 October 1968). Recorded in LD 12:12 for days six to
eight then light-on advanced 4h to give LD 16:8 for days nine to eleven.
LD 20:4, six females, studied from 3-4 days post-emergence (31 October
1968) and recorded for days six to eight.
Results
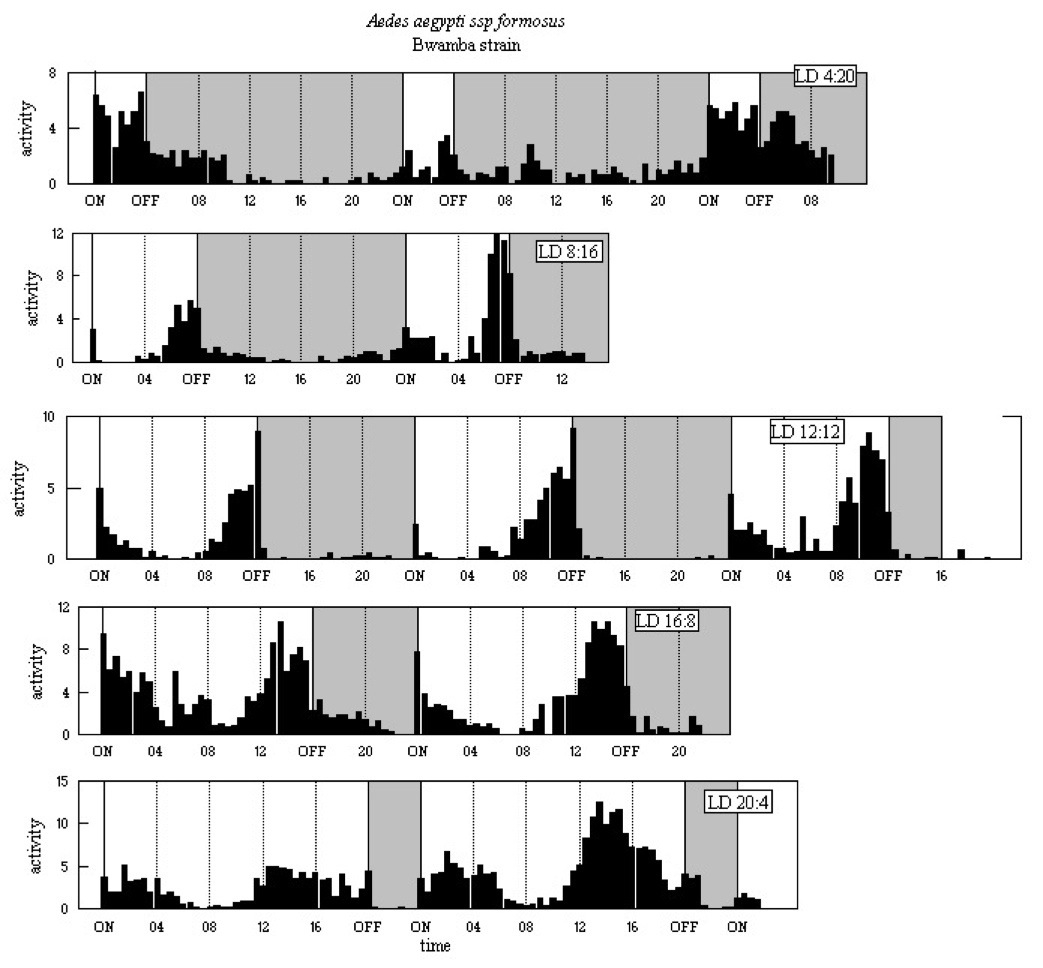
The activity patterns are shown in Figure A3 below.
The pattern in all five LD regimes is dominated by the E' peak.
There is some activity in the subjective night, most obviously in LD
4:20 with a minor peak 3-4h after light-off. There is a clear M peak,
which becomes broader when L > 12h, peaking at 2-2.5 h
after light-on in LD 20:4. It is clear that when L > 14h the E' peak
falls progressively earlier as L increases, coming some 14-15h after
light-on.
Figure A3

|
©1998, 2010 - Brian Taylor CBiol FSB FRES 11, Grazingfield, Wilford, Nottingham, NG11 7FN, U.K. Comments to dr.b.taylor@ntlworld.com |